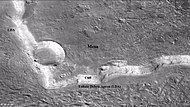
Lobate debris apron
Lobate debris aprons (LDAs) are geological features on Mars , first seen by the Viking Orbiters, consisting of piles of rock debris below cliffs. [1] [2] These features have a convex topography and a gentle slope from cliffs or escarpments, which suggest flow away from the steep source cliff. In addition, lobate debris aprons can show surface lineations as do rock glaciers on the Earth. [3]
Page Revisions
| Year | Metadata | Sections | Top Words | First Paragraph |
| 2018 |
109112 characters 5 sections 28 paragraphs 21 images 657 internal links 15 external links |
lobate 0.446 debris 0.342 ldas 0.336 apron 0.259 lineated 0.245 aprons 0.214 mesa 0.203 ismenius 0.180 brain 0.159 lacus 0.157 hirise 0.120 fill 0.117 hiwish 0.112 ctx 0.111 lda 0.109 |
Lobate debris aprons (LDAs) are geological features on Mars , first seen by the Viking Orbiters, consisting of piles of rock debris below cliffs. [1] [2] These features have a convex topography and a gentle slope from cliffs or escarpments, which suggest flow away from the steep source cliff. In addition, lobate debris aprons can show surface lineations as do rock glaciers on the Earth. [3] |
|
| 2017 |
62682 characters 5 sections 24 paragraphs 22 images 168 internal links 13 external links |
ldas 0.394 lobate 0.381 debris 0.309 lineated 0.287 apron 0.210 aprons 0.201 brain 0.187 mesa 0.167 ismenius 0.159 lacus 0.138 fill 0.138 lda 0.127 cell 0.116 chevron 0.115 reull 0.112 |
Lobate debris aprons (LDAs) are geological features on Mars , first seen by the Viking Orbiters, consisting of piles of rock debris below cliffs. [1] [2] These features have a convex topography and a gentle slope from cliffs or escarpments, which suggest flow away from the steep source cliff. In addition, lobate debris aprons can show surface lineations as do rock glaciers on the Earth. [3] |
|
| 2016 |
60239 characters 5 sections 24 paragraphs 22 images 164 internal links 11 external links |
ldas 0.394 lobate 0.381 debris 0.309 lineated 0.287 apron 0.210 aprons 0.201 brain 0.187 mesa 0.167 ismenius 0.159 lacus 0.138 fill 0.138 lda 0.127 cell 0.116 chevron 0.115 reull 0.112 |
Lobate debris aprons (LDAs) are geological features on Mars , first seen by the Viking Orbiters, consisting of piles of rock debris below cliffs. [1] [2] These features have a convex topography and a gentle slope from cliffs or escarpments, which suggest flow away from the steep source cliff. In addition, lobate debris aprons can show surface lineations as do rock glaciers on the Earth. [3] |
|
| 2015 |
59432 characters 5 sections 24 paragraphs 22 images 165 internal links 10 external links |
lobate 0.388 debris 0.315 lineated 0.293 ldas 0.292 lda 0.228 apron 0.215 aprons 0.205 brain 0.191 mesa 0.170 ismenius 0.162 lacus 0.140 fill 0.140 cell 0.118 chevron 0.118 reull 0.115 |
Lobate debris aprons (LDAs) are geological features on Mars , first seen by the Viking Orbiters, consisting of piles of rock debris below cliffs. [1] [2] These features have a convex topography and a gentle slope from cliffs or escarpments, which suggest flow away from the steep source cliff. In addition, lobate debris aprons can show surface lineations as do rock glaciers on the Earth. [3] |
|
| 2013 |
51309 characters 4 sections 17 paragraphs 14 images 167 internal links 9 external links |
ldas 0.421 lobate 0.349 lineated 0.295 debris 0.295 aprons 0.221 apron 0.171 chevron 0.169 reull 0.165 brain 0.157 phlegra 0.155 deposits 0.128 ice 0.118 glaciers 0.115 floor 0.108 movement 0.106 |
Lobate debris aprons (LDAs) are geological features on Mars , first seen by the Viking Orbiters, consisting of piles of rock debris below cliffs. [1] [2] These features have a convex topography and a gentle slope from cliffs or escarpments, which suggest flow away from the steep source cliff. In addition, lobate debris aprons can show surface lineations as do rock glaciers on the Earth. [3] |
|
| 2012 |
25448 characters 4 sections 13 paragraphs 8 images 31 internal links 7 external links |
ldas 0.426 lobate 0.389 debris 0.321 aprons 0.261 lineated 0.256 apron 0.174 chevron 0.172 reull 0.167 phlegra 0.157 deposits 0.129 ice 0.120 glaciers 0.117 floor 0.109 movement 0.108 slope 0.105 |
Lobate debris aprons (LDAs) are geological features on Mars , first seen by the Viking Orbiters, consisting of piles of rock debris below cliffs. [1] [2] These features have a convex topography and a gentle slope from cliffs or escarpments, which suggest flow away from the steep source cliff. In addition, lobate debris aprons can show surface lineations as do rock glaciers on the Earth. [3] |
|
| 2011 |
25399 characters 4 sections 13 paragraphs 8 images 31 internal links 7 external links |
ldas 0.426 lobate 0.389 debris 0.321 aprons 0.261 lineated 0.256 apron 0.174 chevron 0.172 reull 0.167 phlegra 0.157 deposits 0.129 ice 0.120 glaciers 0.117 floor 0.109 movement 0.108 slope 0.105 |
Lobate debris aprons (LDAs) are geological features on Mars , first seen by the Viking Orbiters, consisting of piles of rock debris below cliffs. [1] [2] These features have a convex topography and a gentle slope from cliffs or escarpments, which suggest flow away from the steep source cliff. In addition, lobate debris aprons can show surface lineations as do rock glaciers on the Earth. [3] |
|
| 2010 |
17228 characters 4 sections 12 paragraphs 8 images 25 internal links 4 external links |
ldas 0.382 lobate 0.338 debris 0.302 lineated 0.255 chevron 0.205 reull 0.200 phlegra 0.187 aprons 0.178 apron 0.166 ice 0.143 glaciers 0.140 colonists 0.135 deposits 0.132 movement 0.129 slope 0.125 |
Lobate debris aprons (LDAs) are geological features on Mars , first seen by the Viking Orbiters, consisting of piles of rock debris below cliffs. These features have a convex topography and a gentle slope from cliffs or escarpments, which suggest flow away from the steep source cliff. In addition, lobate debris aprons can show surface lineations as do rock glaciers on the Earth. [1] |
|
| 2009 |
16360 characters 3 sections 10 paragraphs 9 images 18 internal links 4 external links |
lobate 0.348 debris 0.311 apron 0.214 lineated 0.210 reull 0.206 ldas 0.197 chevon 0.194 phlegra 0.193 aprons 0.184 lda 0.175 deposits 0.159 hellas 0.154 ice 0.147 glaciers 0.144 colonists 0.139 |
Of interest from the days of the Viking Orbiters are piles of material surrounding cliffs. These deposits of rock debris are called lobate debris aprons (LDAs). These features have a convex topography and a gentle slope from cliffs or escarpments; this suggests flow away from the steep source cliff. In addition, lobate debris aprons can show surface lineations just as rock glaciers on the Earth. [1] Recently, research with the Shallow Radar on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter has provided strong evidence that the LDAs in Hellas Planitia are glaciers that are covered with a thin layer of rocks. [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] Radar from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter gave a strong reflection from the top and base of LDAs, meaning that pure water ice made up the balk of the formation (between the two reflections). [7] Based on the experiemnts of the Phoenix lander and the studies of the Mars Odyssey from orbit, frozen water is know to exist a just under the surface of Mars in the far north and south (high latitudes). The discovery of water ice in LDA's demonstrates that water is found at even lower latitudes. Future colonists on Mars will be able to tap into these ice deposits, instead of having to travel to much higher latitudes. Another major advantage of LDA's over other sources of Martian water is that they can easily detected and mapped from orbit. Lobate Debris Aprons are shown below from the Phlegra Montes which are at a latitude of 38.2 degrees north. The Phoenix lander set down at about 68 degrees north latitude, so the discovery of water ice in LDA's greatly expands the range of easily available on Mars. [8] It is far easier to land a spaceship near the equator of Mars, so the closer water is available to the equator the better it will be for future colonists. |